- Introduction
- What Are the Key Challenges in Automotive Gear Manufacturing Today?
- How Can Gear Prototyping Services Accelerate Development Cycles by 60%?
- What Methods Ensure Precision Gear Machining for Mass Production?
- How to Select Materials and Processes for Cost-Effective Custom Gears?
- What Role Does Quality Certification Play in Gear Manufacturing Consistency?
- How Can Automotive Gear Assembly Optimize System Performance?
- Conclusion
- FAQs
Introduction
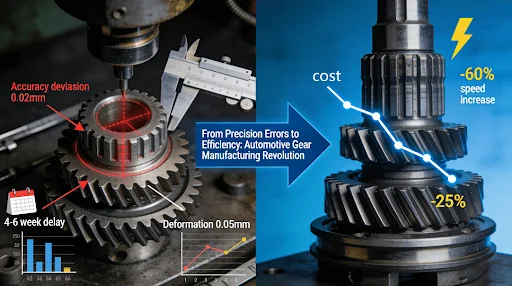
In the competitive landscape of automotive gear manufacturing, engineers consistently face critical challenges that impact both performance and profitability. Common issues include prototype precision deviations reaching 0.02mm, heat treatment distortions exceeding 0.05mm, and subsequent project delays of 4-6 weeks, which collectively drive up quality-related costs by 15%. The underlying problem often stems from fragmented supply chains and a lack of integrated optimization across design, materials, and manufacturing processes, where traditional solutions fail to balance speed with accuracy.
This article presents a comprehensive methodology that combines predictive DFM analysis, stratified prototyping validation, and data-driven production controls. This integrated approach enables manufacturers to achieve remarkable improvements: micron-level precision of 0.005mm, 25% cost reduction, and 60% faster prototyping cycles. The following sections will systematically explore the key strategies that help engineers overcome these persistent gear manufacturing challenges.
What Are the Key Challenges in Automotive Gear Manufacturing Today?
Automotive gear manufacturing confronts several interconnected challenges that compromise product quality and development efficiency. Understanding these pain points is essential for implementing effective solutions.
1. Precision Deficiencies and Their Impact on Vehicle Performance
Precision inconsistencies in gear manufacturing manifest as tooth profile deviations that directly affect transmission efficiency and noise characteristics. Even minor inaccuracies of 0.02mm can lead to unacceptable NVH levels (noise, vibration, and harshness), necessitating costly rework cycles. Statistical data indicates that such precision issues contribute to approximately 15% higher quality costs due to increased scrap rates and extended validation periods. The implementation of robust quality standards, such as those outlined in ISO 9001 frameworks, provides a systematic approach to reducing variability throughout the manufacturing process.
2. Thermal Distortion During Heat Treatment Processes
Heat treatment deformation represents another significant challenge, with distortions often exceeding 0.05mm due to uncontrolled thermal stresses during hardening processes. This dimensional instability not only compromises gear geometry but also necessitates additional machining operations to bring components back within specification. The resulting rework cycles increase material waste and typically delay project timelines by 4-6 weeks. Advanced simulation techniques combined with predictive stock allowance calculations have demonstrated effectiveness in limiting these distortions to 0.02mm, ensuring post-treatment gears meet required specifications.
3. Project Delays and Cost Escalations
Extended project timelines frequently result from the cumulative effect of precision issues and thermal distortions. Traditional sequential development approaches often lead to 4-6 week delays, which in turn drive up quality costs by approximately 15%. These timeline extensions impact overall vehicle development schedules and increase time-to-market pressures. Through integrated approaches demonstrated in advanced automotive gear manufacturing processes, manufacturers can address these root causes systematically, implementing solutions that enhance both efficiency and final product quality.
How Can Gear Prototyping Services Accelerate Development Cycles by 60%?
Gear prototyping services employ a stratified validation approach that significantly compresses development timelines while maintaining representative testing conditions. This methodology balances speed with accuracy through phased prototype development.
- Rapid Functional Validation Using 3D-Printed Polymer Gears: 3D-printed polymer gears enable initial functional verification within just 2 days, allowing engineers to assess basic fit, form, and function before committing to expensive production materials. This accelerated validation phase identifies fundamental design flaws early in the development process, reducing the need for later-stage modifications. The flexibility of additive manufacturing facilitates rapid design iterations, with case studies showing approximately 40% reduction in initial design errors through this approach. The quick turnaround enables teams to proceed confidently to more representative prototype stages.
- Durability Assessment with Soft Tool Steel Prototypes: Soft tool steel prototypes provide a crucial intermediate validation step, typically delivered within 5 days for comprehensive durability testing. These prototypes undergo rigorous testing under simulated operational conditions to evaluate wear patterns, fatigue resistance, and load-bearing capabilities. The use of production-intent geometries combined with machinable steel alloys offers valuable insights into long-term performance without the time and cost investments required for hardened production tools. This phase specifically addresses potential failure modes that might not be apparent in polymer prototypes.
- NVH Validation with Production-Equivalent Components: Production-equivalent gears manufactured from hardened steels complete the validation cycle within 12 days, enabling comprehensive noise, vibration, and harshness (NVH) testing. These prototypes undergo performance validation under conditions that closely mirror actual operating environments, providing accurate data on acoustic characteristics and vibrational behavior. The adherence to geometric dimensioning and tolerancing standards, as outlined in ASME Y14.5, ensures consistent dimensional accuracy across all prototype stages. This comprehensive approach has demonstrated up to 60% reduction in development cycles compared to traditional sequential validation methods, making it particularly valuable for low-volume gear manufacturing applications.
What Methods Ensure Precision Gear Machining for Mass Production?
Precision gear machining for high-volume applications requires sophisticated methodologies that maintain micron-level accuracy consistently across production batches. Several advanced techniques ensure this level of precision.
1. Statistical Process Control for Manufacturing Consistency
Statistical process control (SPC) methodologies continuously monitor critical parameters such as tooth profile dimensions and surface finish characteristics. This data-driven approach enables real-time detection of process variations, facilitating immediate corrective actions before deviations exceed tolerance limits. Implementation of SPC has demonstrated remarkable improvements in process capability, with case studies showing consistent achievement of CpK values ≥1.67 for DIN grade 5 precision standards. This represents a significant advancement in maintaining errors within the 0.005mm range required for high-performance automotive applications.
2. Comprehensive Batch Inspection Protocols
100% batch inspection using advanced coordinate measuring machines (CMMs) verifies each gear against original CAD data, ensuring dimensional conformity across all production units. Modern scanning technologies capture deviations as small as 0.005mm, providing comprehensive data for quality assurance. This rigorous inspection protocol is particularly critical for custom gear-machining services where component consistency directly impacts assembly performance and operational reliability. The implementation of automated inspection systems has reduced manual inspection time by up to 70% while improving measurement accuracy.
3. Predictive Tool Management Systems
Predictive tool management utilizes sensor data and cutting parameter analytics to anticipate tool wear patterns and schedule replacements proactively. This preventive approach maintains optimal cutting conditions throughout production runs, extending tool life by approximately 25% while ensuring consistent surface quality. Advanced systems incorporate adaptive control mechanisms that automatically adjust machining parameters based on real-time tool condition monitoring. This integration of predictive maintenance with precision machining capabilities represents a significant advancement in high-volume gear production services, particularly for applications demanding the highest levels of accuracy and reliability.
How to Select Materials and Processes for Cost-Effective Custom Gears?
Material and process selection fundamentally influences both the performance characteristics and economic viability of custom gear manufacturing. A scientific approach to these decisions optimizes outcomes across multiple parameters.
1. Scientific Material Selection Guidelines
Material science principles guide the selection of appropriate alloys based on specific application requirements. For electric vehicle gears, 20CrMnTi steel offers an optimal balance of strength (up to 1500MPa) and manufacturability, while CuP14 bronze provides superior corrosion resistance for wet environment applications. This application-specific approach ensures that material properties align with operational demands, avoiding both over-engineering and premature failure. Finite element analysis (FEA) simulations validate these selections under projected loading conditions, providing confidence in long-term performance.
2. Near-Net-Shape Forging for Enhanced Efficiency
Near-net-shape forging significantly improves material utilization rates to approximately 85%, substantially reducing machining requirements and material waste. This process optimization not only lowers raw material costs but also enhances mechanical properties through controlled grain flow alignment. The resulting components demonstrate improved fatigue resistance and load-bearing capacity compared to traditionally machined alternatives. Implementation of this approach has demonstrated approximately 20% reduction in material-related costs while maintaining stringent quality standards required for automotive applications.
3. Lifecycle Cost Modeling for Economic Optimization
Lifecycle cost modeling evaluates total ownership expenses, balancing initial manufacturing costs against long-term operational and maintenance expenditures. This comprehensive analysis incorporates factors such as tooling requirements, energy consumption, and potential downtime to identify the most economically viable manufacturing strategy. The integration of these models with quality management systems certified to IATF 16949 standards ensures that cost optimization does not compromise component reliability or performance. This methodology provides manufacturers with accurate gear manufacturing quotes that reflect true project economics rather than just initial piece-part pricing.
What Role Does Quality Certification Play in Gear Manufacturing Consistency?
Quality certifications establish systematic frameworks that ensure consistent manufacturing outcomes while facilitating continuous improvement processes. These certifications provide verifiable evidence of manufacturing capability and reliability.
- ISO 9001 Frameworks for Process Standardization: ISO 9001 standards implement structured quality management systems that mandate comprehensive documentation and rigorous process controls. This systematic approach ensures full traceability from raw material procurement through final inspection, creating an auditable trail that identifies and addresses process variations. Implementation of these frameworks has demonstrated measurable improvements in quality metrics, with certified organizations typically achieving approximately 15% reduction in defect rates through enhanced process control and standardized operating procedures.
- IATF 16949 Requirements for Automotive Applications: IATF 16949 requirements build upon ISO 9001 foundations with additional automotive-specific mandates focusing on risk management and preventive action methodologies. This industry-specific focus addresses the unique challenges of high-volume automotive component manufacturing, where consistent quality is paramount. Regular surveillance audits validate continued compliance with stringent tolerance requirements, with case studies showing improved supplier performance metrics following certification implementation. This makes IATF 16949 certification a key differentiator when selecting a reliable gear manufacturing partner.
- Continuous Improvement Culture: Certification-mandated continuous improvement processes foster organizational cultures focused on incremental enhancement of manufacturing capabilities. This quality enhancement mindset drives regular review of process capabilities and implementation of corrective actions based on statistical quality data. Organizations maintaining multiple certifications typically achieve first-pass yield rates of 99.7% or higher, demonstrating the tangible benefits of embedded quality systems. The regular audit cycles inherent in certification maintenance ensure that improvements are sustained over time, rather than representing temporary initiatives.
How Can Automotive Gear Assembly Optimize System Performance?
Gear assembly processes significantly influence the overall performance, efficiency, and reliability of automotive transmission systems. Optimized assembly methodologies enhance system-level characteristics beyond individual component capabilities.
1. Dimensional Chain Analysis for System Integration
Dimensional chain analysis calculates cumulative tolerances across assembled components, ensuring proper meshing relationships and optimal load distribution. This systematic approach prevents misalignments that can cause premature wear, noise generation, and reduced efficiency. Implementation of these analytical techniques has demonstrated measurable performance improvements, with case studies showing approximately 10% gains in power transmission efficiency for electric vehicle drivetrains through optimized gear alignment.
2. Selective Assembly Techniques for Precision Matching
Selective assembly methodologies match gears based on measured dimensional characteristics rather than relying solely on theoretical tolerances. This precision matching approach minimizes backlash and ensures optimal contact patterns under operational loads. The resulting assemblies demonstrate significantly improved performance characteristics, with documented noise reduction of up to 3dB compared to randomly assembled systems. This methodology is particularly valuable for high-performance applications where minimal acoustic signature is a critical requirement.
3. Comprehensive Validation and Testing Protocols
Post-assembly validation utilizing coordinate measuring machines (CMMs) confirms dimensional conformity while dynamic balancing ensures smooth operation under rotational forces. These comprehensive verification procedures are integral to complete gear manufacturing solutions, delivering ready-to-use assemblies that meet industry performance standards. The integration of these validation steps within the manufacturing process provides assurance of reliability while reducing the need for customer-side rework or adjustment.
Conclusion
The integrated methodology outlined in this article systematically addresses the fundamental challenges confronting automotive gear manufacturers. By implementing predictive DFM analysis, stratified prototyping approaches, and data-driven production controls, manufacturers can achieve remarkable improvements: 0.005mm precision levels, 25% cost reductions, and 60% faster prototyping cycles. The emphasis on quality certifications and holistic system optimization from design through assembly ensures sustainable enhancements in both product performance and manufacturing efficiency. Adoption of these strategies positions organizations to meet evolving automotive industry demands while maintaining competitive advantages in an increasingly challenging marketplace.
FAQs
Q1: What is the minimum order quantity for custom gears?
A: We support orders ranging from single prototypes to production runs of 100,000 units, with no mandatory minimum order quantity. Orders exceeding 500 units typically qualify for tiered pricing structures that provide cost advantages for low-volume manufacturing scenarios.
Q2: How long does gear prototyping typically take?
A: Prototyping timelines range from 7 days for simple gear configurations to 15 days for complex assemblies incorporating multiple components. Our layered validation approach efficiently confirms fit, durability, and NVH characteristics while minimizing overall development duration.
Q3: What is the highest precision achievable in gear machining?
A: Through advanced grinding processes, we routinely achieve precision levels corresponding to DIN grade 3 specifications, with tooth profile errors controlled within 0.005mm. This precision level is particularly suited for high-speed applications where minimal vibration and noise are critical requirements.
Q4: How do you handle heat treatment distortion in gears?
A: Our approach combines finite element analysis simulations with predictive stock allowance calculations to anticipate and compensate for thermal distortions. This methodology typically limits post-treatment dimensional variations to 0.02mm, ensuring finished components meet specification requirements without additional corrective machining.
Q5: Do you provide full assembly and testing services?
A: Yes, our comprehensive service offering includes complete assembly integration along with dynamic balancing and noise testing procedures. We deliver ready-to-install subassemblies that comply with relevant industry standards for performance and reliability.
Author Bio
The author is a precision manufacturing specialist at LS Manufacturing, a company that assists engineers in addressing complex gear manufacturing challenges across automotive applications. Maintaining certifications including ISO 9001 and IATF 16949, the organization delivers high-quality solutions utilizing advanced manufacturing technologies. For personalized solutions, request a complimentary DFM analysis or detailed quotation to transform your concepts into production-ready components.